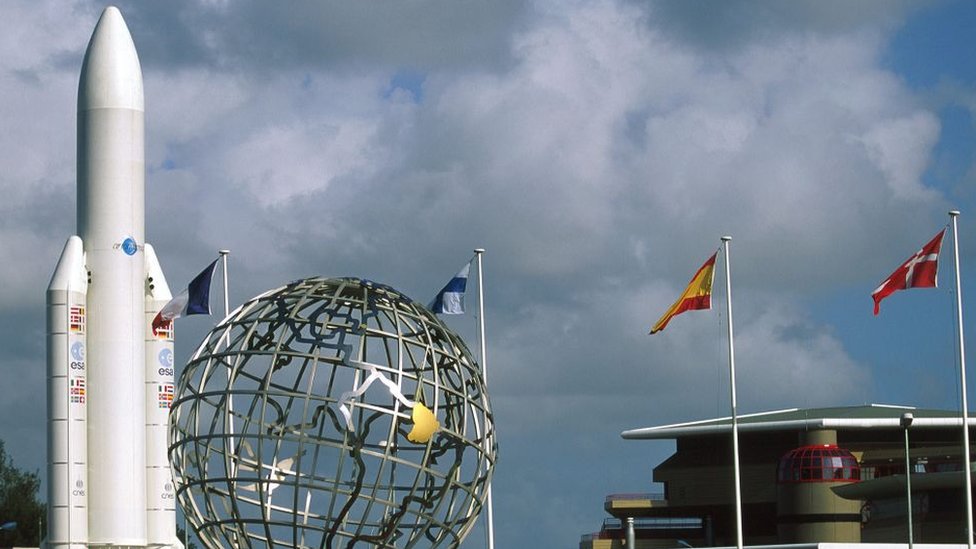
It is a small region in continental South America, with an area of only 83,846 square kilometers. But within its borders includes one of the space ports From Europe: An koro, jointly managed by European Space Agency (ESA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), and Arianespace.
French Guiana, with a population of about 2591,109 and a very low population density, is a major center of the space race, not only in Europe, but also globally.
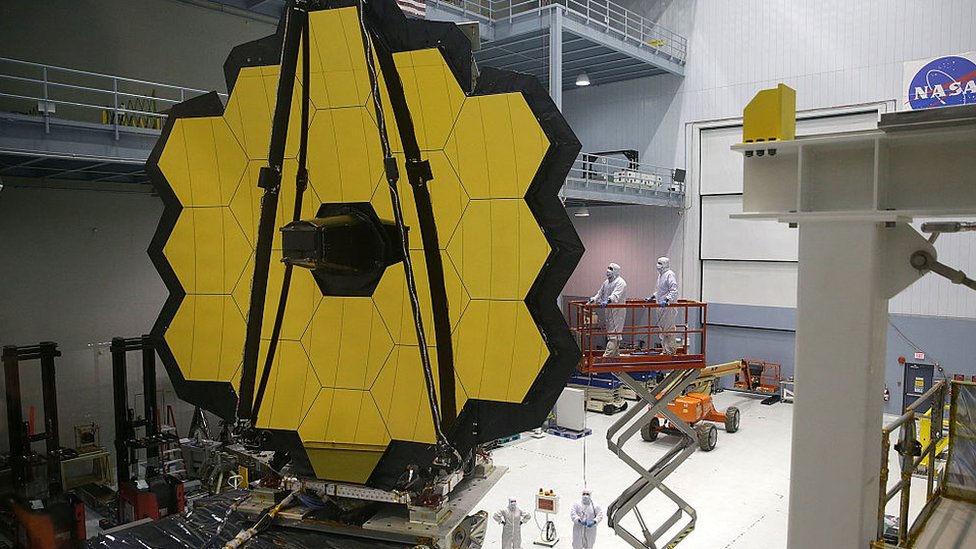
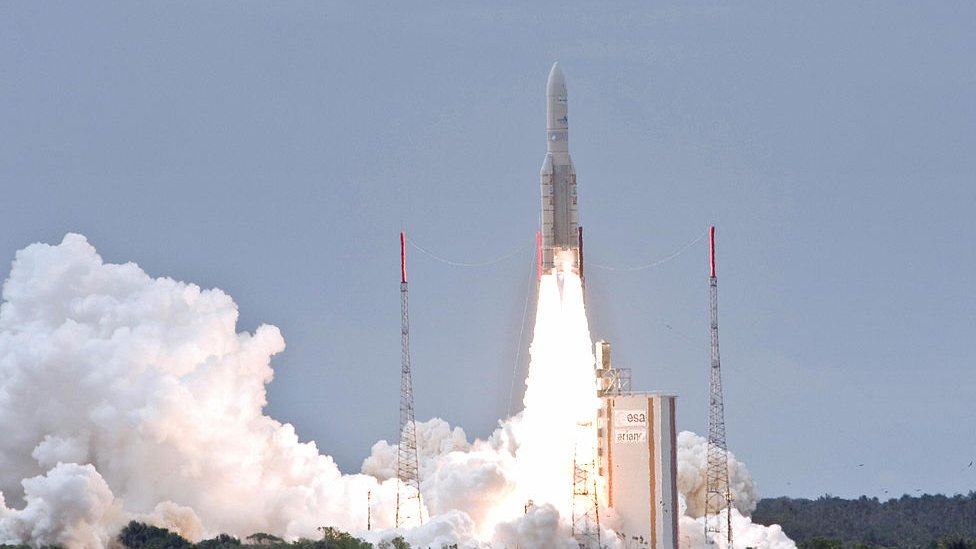
And it’s from here specifically, where it will launch on Saturday, December 25th James Webb Telescope aboard an Ariane 5 rocket.
As the successor to NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, James Webb was designed to look deeper into the universe and, as a result, to detect events that occur much later, more than 13.5 billion years ago.
Scientists also hope to use their most advanced capabilities to study the atmospheres of distant planets in the hope that they will be able to detect signs of life.
At a cost of 10,000 USD Million dollar construction over 30 yearsThe project is jointly led by NASA and the European Space Agency.
Shortly after launch, the Webb rocket will launch on a trajectory that will take it to a control station 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. On this trip, which should last for a month, the telescope will deploy its 6.5-meter primary mirror and a shield to protect its observations of the universe from sunlight and heat.
Web goal is Get pictures of the first bodies formed after the Big Bang.
Everything will be managed from the control room located in Kourou.
“I can say that (European Spaceport) has one of the best locations in the world in terms of suitability for launching into space,” mission director Giulio Abrea told BBC Mundo.
European territory in South America
In 1964, France had to choose a site from which to launch its satellites. The European country no longer enjoys Algeria, which gained independence in 1962.
14 sites were analyzed until experts chose kuru, A town within French Guiana located 55 kmómeters from the capitalAnd CayenneAnd And 500 km fromINi from Ecuador.
There were many aspects that were evaluated, from historical, political to technical.
This area, inhabited by European settlers since the 17th century and once a penal center, officially became an overseas department of France in 1946.
The geopolitical aspect is very important. That French Guiana is part of the European continent – the official language is French and the currency is the Euro, and despite being located in northeastern South America, it simplifies things.
Finally, in 1975, the French government made a decision to share it Guyanai Spatial CenterWith the newly created ESA.
Spaceport in the middle of the forest
But its strategic location on the map is ideal for space scientists and engineers.
More than 90% of the country is covered with tropical forests. This represents a safety feature in the event of accidents.
It is also not affected by cyclones or hurricanes, because these form mas towards the Caribbean Sea.
On the other hand, French Guiana has a north and east coast that is inundated with the waters of the Atlantic Ocean. In this way, the launch angle is 102 degrees, which allows it to perform all possible space missions.
Aprea explains: To get pitches for ógeostationary transfer orbitWhere most communications satellites are located, the missiles must take off towards the east.
But on the way to space, the rocket “thrown” layers that fall into uninhabited places. In the case of French Guiana, this place goes around the ocean.
Read also: They discovered 70 wandering planets, which may have been expelled from their solar system
But it’s also easy to launch ópolar orbits From here heading northwest. These orbits are synchronized with the Sun, which means that a satellite in this orbit will pass through the same point on Earth at the same time every day.
“If the sun is always in the same position, and the shadows are always the same, then you can better analyze the different changes. If you instead go through the same point, but have different positions of the sun, the shadows change and it will change is much more. It’s hard to analyze What you see,” explains Aprea.
One of the most important launches from Koro was the first (1968), the rocket launch Europe 2 (1971), and Ariane 1 (1979, ESA’s first successful rocket), rocket launch Soyuz (2011) and vega (2012).
slingshot effect
Another feature of the European Spaceport is what scientists know slingshot effect‘ or ‘slingshot effect’ (slingshot, slingshot or slingshot in some countries).
This happens precisely because The port is close to the equator.
the “slingshot fect” is being The energy generated by the speed of the Earth’s rotation around the poles axis.
But the following happens: the closer an object is to the equator, the faster it moves.
This happens because of An object in the middle of the world should spin faster From one located at the poles of the planet.
The Earth’s rotation time is about 24 hours. But depending on what latitude it is in, the speed used for an object to complete a rotation can change at that time.
The Ecuador line is 40,075 kilometers long. But as we go towards the poles, the circumferential line gets smaller, so a lower speed is used to complete the rotation in 24 hours.
This energy gives an initial boost to the missiles at the time of takeoff. “Imagine you have two cars that you have to accelerate to 100 km / h. You have two ways: one starts from 0 km / h and the other starts from 30 km / h. Obviously 30 will reach faster. This is what gives you Ecuador ”, explains Abrea.
This initial boost is very useful for space launches, since Saves fuel and weight.
If the launch is carried out at other latitudes, the effect changes and more fuel is consumed. It will also add a significant amount of weight, amounting to hundreds of kilograms, which makes a “big difference,” as Aprea puts it.
“Going up and down is very easy. What takes more work is to go into orbit because you have to go really fast to get to such a speed that you stay in orbit,” says the specialist.
The European Space Agency is already developing an Ariane 6 rocket with which it intends to increase the number of launches. The French Space Agency is preparing the facilities in Kourou for the first launch of this rocket in the second quarter of 2022.
You can now receive notifications from BBC Mundo. Download and activate the new version of our app so you don’t miss our best content.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XT3T-3-D7MI&t=9s
fjb

“Problem solver. Proud twitter specialist. Travel aficionado. Introvert. Coffee trailblazer. Professional zombie ninja. Extreme gamer.”








More Stories
With a surprise in the case: a strange cell phone from Nokia was introduced
PlayStation Stars: what it is, how it works and what it offers to its users | Sony | video games | tdex | revtli | the answers
t3n – Digital Pioneers | digital business magazine