Artificial intelligence is becoming more and more a part of our lives, and according to experiments with 119 participants, robots with human-like behaviors can be considered as endowed with mental states.
When robots appear to interact with people and display human-like emotions, individuals may view them as being able to “think” or act according to their own beliefs and desires rather than their own computer programs, concludes research published in Technology, Mind, and Behavior Journal.
However, the relationship between anthropomorphic shape and human-like behavior and the tendency to attribute independent thinking and purposeful behavior to robots is not yet fully understood, says Agnieszka Wikoska, a researcher at the Italian Institute of Technology and author of the study.
“As AI becomes more and more a part of our lives, it is important to understand how interacting with a robot that exhibits human-like behaviors can lead to a higher probability of attributing the intentional action to the robot.”Add.
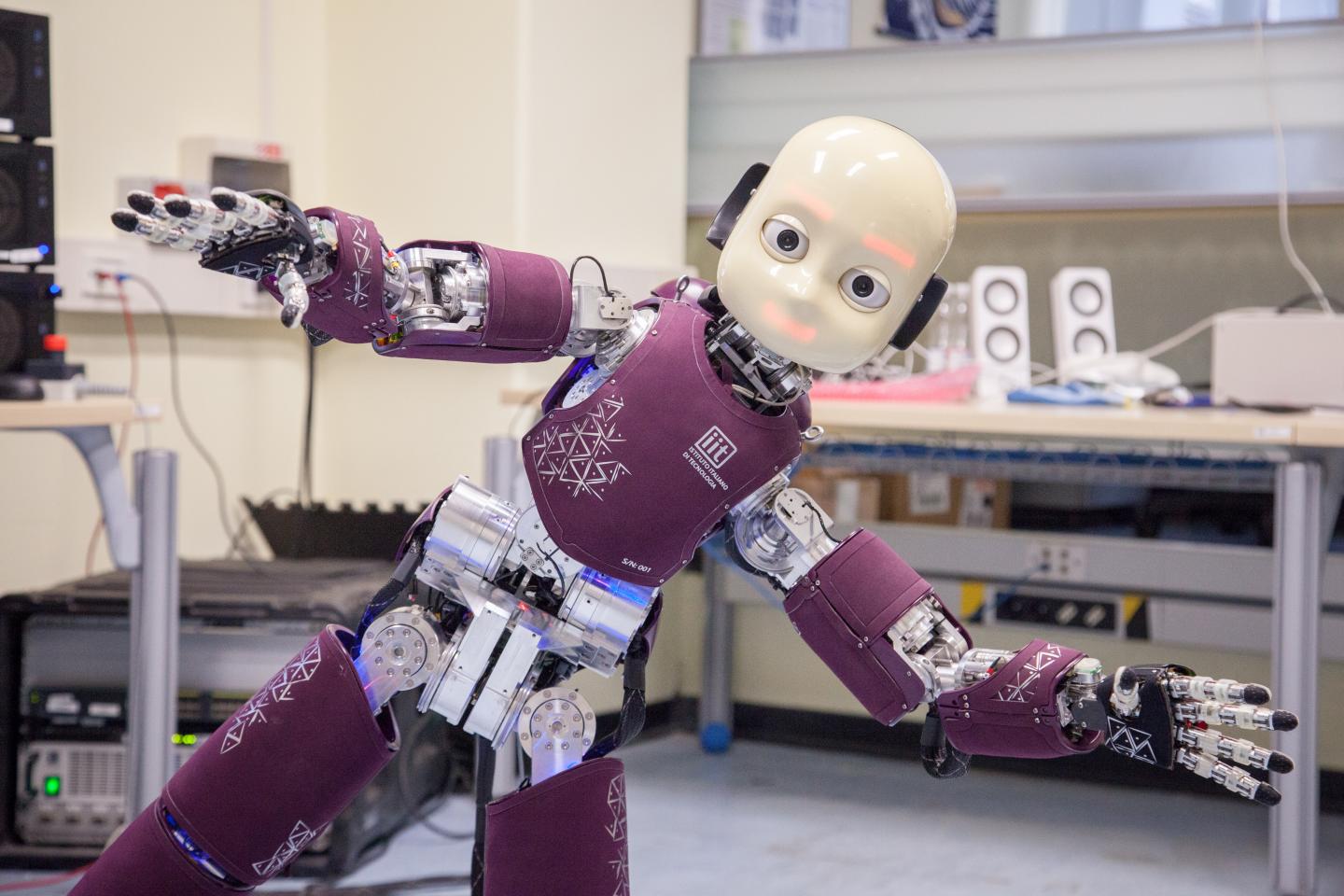
The team conducted three separate tests with 119 participants examining how they perceived a human-like robot, iCub, after socializing with it and watching videos together.
Before and after interacting with the robot, volunteers completed a questionnaire that showed them pictures of the robot in different situations and asked them to choose whether the machine’s drive in each situation was mechanical or intentional.
For example, participants viewed three images showing the robot choosing a tool, then chose whether it “grabbed the nearest object or was intrigued with the tool,” detailing a note from the American Psychological Association.
In the first two experiments, the iCub’s actions were remotely controlled to act in a group manner, greet volunteers, introduce themselves and ask for their names; Cameras in their eyes were able to recognize participants’ faces and maintain eye contact.
Next, the volunteers watched three short documentary videos with the robot, programmed to respond to the videos with sounds and facial expressions of sadness, amazement or happiness.
In the third experiment, the researchers programmed the iCub to act like a machine while watching videos with participants: the cameras in his eyes were turned off so he couldn’t maintain eye contact, and all emotional reactions to the pictures were turned off. Replace with “voice” and repetitive movements of his torso, head and neck.
The team found that participants who watched videos with the human-like robot were more likely to rate the actions of the human-like robot as intentional rather than programmed, while those who only interacted with the more mechanical robot did not.
This shows that mere exposure to a human-like robot is not enough to believe that it is capable of thinking and emotions. It is the human-like behavior that can be critical to being seen as an intentional factor.
According to Wykowska, this could form the basis for the design of social robots in the future: social association with them could be useful in some contexts, such as social assistance robots.
For example, in the care of the elderly, social bonds with the elderly can lead to a greater degree of compliance with recommendations regarding medication intake. EFE

“Problem solver. Proud twitter specialist. Travel aficionado. Introvert. Coffee trailblazer. Professional zombie ninja. Extreme gamer.”



More Stories
With a surprise in the case: a strange cell phone from Nokia was introduced
PlayStation Stars: what it is, how it works and what it offers to its users | Sony | video games | tdex | revtli | the answers
t3n – Digital Pioneers | digital business magazine