Exactly two seconds after 22:21 local time (Wednesday 7:21 Polish time), a Falcon 9 carrier rocket was launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in Southern California. For the first time in history, it will deliberately collide with an asteroid.
This is the start of the DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission. The first ever planetary defense mission to see if in the future NASA will be able to protect Earth from the deadly effects of an asteroid impact.
NASA launches DART mission
55 seconds after take-off, the Falcon 9 rocket reached the speed of sound, and after 2 minutes 38 seconds, the first stage of the rocket (the so-called booster) separated from the second stage, which continued to launch. DART ship into space. 6.5 minutes later, the booster landed on the “Of Course I Still Love You” craft in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of California. This was the third successful landing of this specimen.

More about the DART mission can be found on the main page Gazeta.pl
After liftoff, NASA and SpaceX started the second stage engine twice, and 55 minutes and 48 seconds after liftoff, the DART probe and the second stage rocket separated. After an hour and 9 minutes, NASA scientists were able to get direct contact with the ship. It now begins its only journey towards the asteroid system Didymos (more on that in a moment).
The ship now has several billion to go kilometers. Over the coming months, the asteroids Didymos and Demorphos will “chase” in their orbit around the Sun. It will catch up with them in September 2022, when the asteroids are relatively close to Earth. The asteroid will likely hit on September 24th.
NASA will cause a space disaster. on Dimorphos
Didymos and Demorphos are two small asteroids that orbit a common center of mass together while orbiting the sun in a close collision course with our planet. They are classified as near-Earth asteroids and dangerous asteroids. Didymus is larger (780 m in diameter) and smaller Demorphos (170 m) meters diameter) is its moon.
NASA plans to hit smaller asteroids. The DART spacecraft, weighing about 670 kg, will be directed on a collision course with a cosmic rock and will hit its surface at a speed of 6.6 km / s, which is less than 24 thousand. how many hours. This should have little effect on the speed of Demorphos, which orbits a center of mass shared with the asteroid Didymos.
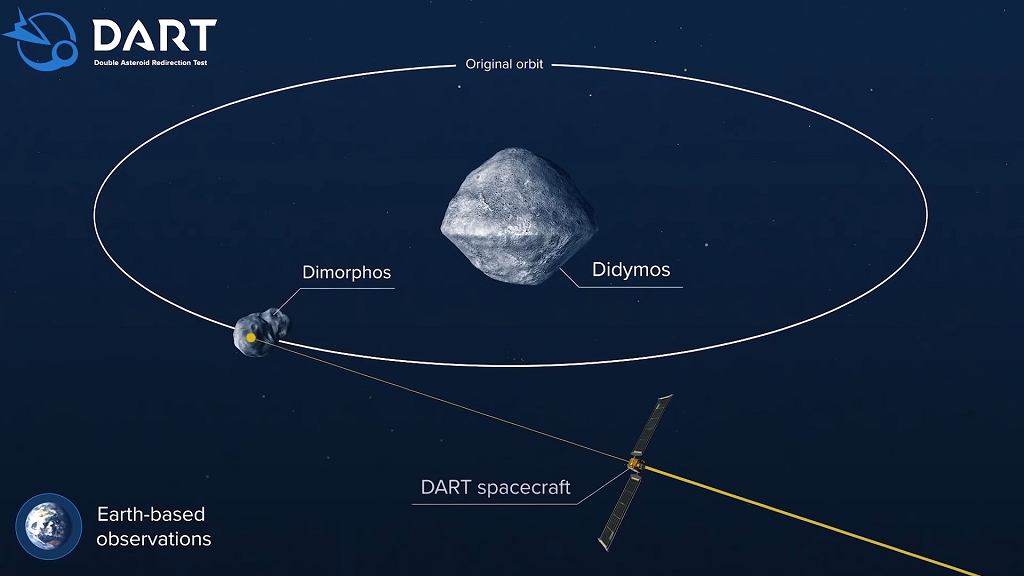
Scientists estimate the drop in velocity to be about 1/5 of a millimeter per second. Dimorphos should move around their companion much slower (at a speed of several kilometers/sec) after impact. That’s an insanely small change, but as NASA points out, even small changes in space have big impacts.
A blow over time will affect the orbit of the asteroid, which will become more and more different from the original orbit over time. According to the researchers, the difference is likely to be noticeable after a few months. Scientists will measure this very precisely with the help of ground-based telescopes that monitor the transit of the smaller asteroid (against the background of the larger asteroid). By comparing the observations with pre-collision data, they will calculate the impact of the task over the object’s orbit.
We will have an “eye” in space
The same effect will also be recorded by the DRACO (Reconnaissance Camera and Asteroid Camera for Photonavigation) – DART’s only research instrument. In addition, a 14-kilogram LICIACube mini-satellite created by researchers from the Italian Space Agency will be housed in a spring cassette inside the ship.
10 days prior to impact, LICIACube will separate from the DART vessel and observe the impact from a safe distance, transmitting the collected data directly to Earth. It is to record images of the collision, the dust plume from the collision, and the crater on the surface of the asteroid.
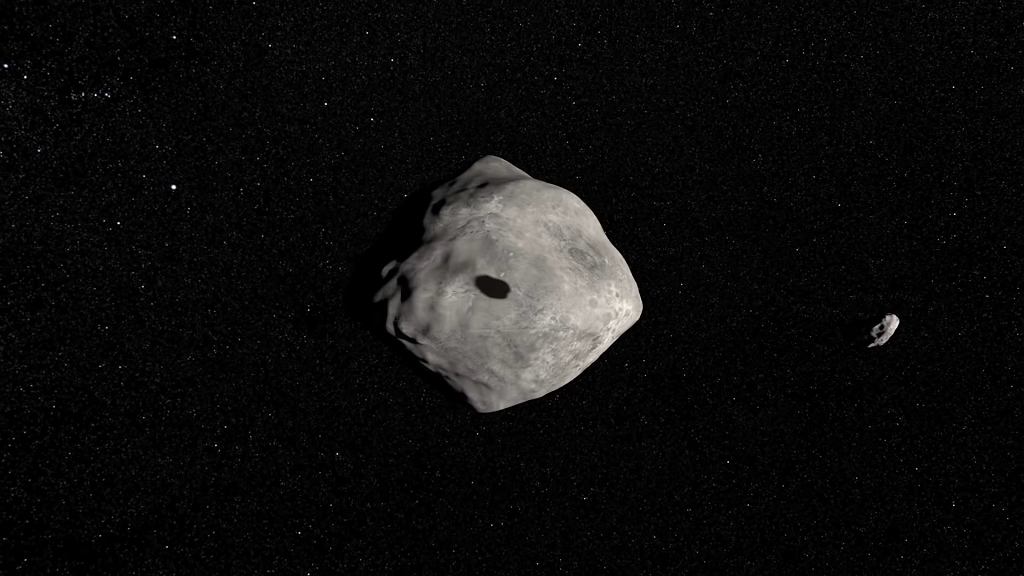

DART is a realistic public test to see if we are actually able to influence the asteroid’s orbit. NASA (and other space agencies, too) hope that in the future people will be able to “push” asteroids into Earth collision cycles.
Experts assert that we do not currently know of any object that directly threatens the Earth. However, in history our planet has already been hit by many asteroids that greatly affected life on Earth. It is possible that sooner or later another person will emerge from outer space.



More Stories
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090: AIDA64 gets Ada spearhead support
Rogue Trader – Details about the first cRPG in the series – CD-Action
t3n – Digital Pioneers | digital business magazine